The more we rely on email, the more susceptible we are to spam and phishing attempts by cyber frauders. Recently, yet another company lost 3.8 million when they made a bank transfer requested by a spoofed email. How did it happen?
The attackers set up an email account that mirrored [Alutiiq CEO] Hambright’s email address and sent an email to Alutiiq’s controller that gave instructions about a “confidential transaction” by a person who called minutes later.
Pretending to be an attorney, the co-conspirator requested an “urgent” transfer of the $3.8 million “to an entity later revealed to be a fictitious third party company based in Hong Kong,” Hambright wrote. Hambright and the chief financial officer discovered the transfer two days later.
All companies small and large are susceptible to scams like this. Fortunately for Office 365 users, there is an easy way to effectively block spam and spoofing attempts by blocking senders from “Outside the organization”. Microsoft TechNet Blogger Caltaru Mihai also mentions this technique near the end of his Block Spoofing in Office 365 post and appropriately cautions “that this is a dangerous rule if not configured correctly, but it is very effective at blocking spoofing“.
Office 365 Exchange Admin Center
- Log into your Office 365 Exchange Admin Center
- Navigate to mailflow, then rules, and add a new rule
- Click “More Options…” near the bottom of the new window
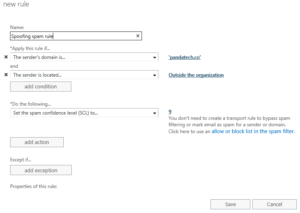
- Add two conditions:
The sender’s domain is… yourdomain.com
AND
The sender is located… Outside the organization - Add one action:
Reject the message with the explanation… Message has been blocked as an email spoofing attempt.
Or
Modify the message properties… Set the spam confidence level (SCL) to… 9
- Add an exception(s)
- This is not necessary, but it is usually a good idea to whitelist your company’s WAN IPs as well as any other legitimate services that may be sending emails on your company’s behalf. If you have SPF set up, then you can use the same IPs listed in the SPF TXT record

Let me know if this rule works out for your organization, or if you find some new ways to improve it!